CEO Guide to Human Rights
This CEO Guide is a call to action to our peers.
It provides insight into how companies are meeting the corporate responsibility to respect human rights, and shares actions business leaders are taking to get ahead, and stay ahead, in this crucial space.




































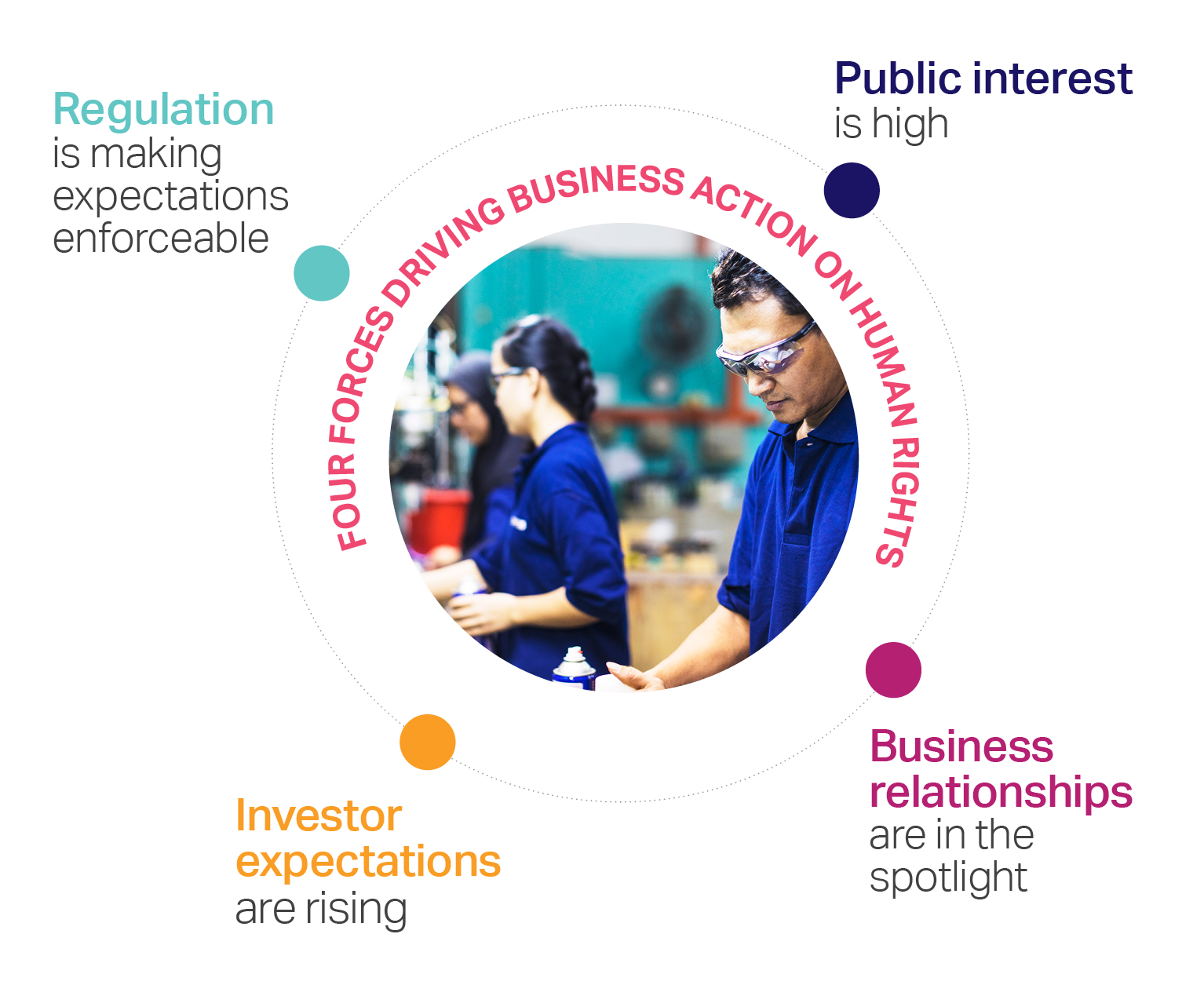
Companies affect human rights every day in their interactions with employees, suppliers, consumers, partners and communities
The business responsibility is clear
The three pillars of the UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights:
PROTECT
States have a duty to protect people against human rights abuses by third parties, including business.
They are expected to prevent, investigate, punish and redress abuses through policies, legislation, regulation
RESPECT
Business has a responsibility to respect human rights.
It should address adverse human rights impacts that may result from its own activities and its business relationships.
REMEDY
Affected people must be able to access remedy.
Both states and business have roles to play in ensuring access to remedy when negative impacts occur.
A company’s responsibility to respect human rights encompasses:
- Its own operations, including joint ventures and other forms of partnerships.
- Its business relationships with public and private entities in its value chain, including suppliers, labor contractors, distributors and business customers.
Practical actions are well defined
How business is expected to implement the respect and remedy pillars:
POLICY
Commit to respect human rights
Embed human rights policy in the company’s culture
HUMAN RIGHTS DUE DILIGENCE
Identify potential and actual human rights impacts
Act upon the findings
Track company’s performance on preventing and mitigating impacts
Communicate the company’s efforts
REMEDIATION
Establish operational-level grievance mechanisms
Provide for or cooperate in remediation
Action points for CEOs to advance respect for human rights
KNOW the most important human rights for your company
Identify risks to people and assess their relative severity, especially by listening closely to those affected by the company’s products and services, operations and supply chains.
Keep track of emerging hot topics, by industry (e.g. cobalt supply chains in electronics and e-vehicle battery manufacturing) and public attention level (e.g. #metoo).
Be prepared to communicate on challenges faced and the company’s efforts to continuously improve.
LEAD from the top
Send a clear and unequivocal human rights message to staff across the organization, from R&D to procurement to sales and marketing, to present a shared vision.
Empower staff to set clear expectations in their dealings with business partners whose practices can impact human rights.
Provide the performance objectives, incentives, and resources staff need to address human rights issues
ENGAGE transparently with stakeholders
Demonstrate that your company values its relationships with people and society by being personally aware, prepared and willing to take action.
Listen directly to stakeholders whom your business can impact to understand their perspectives and the difference your decisions and actions can make to their lives.
Share your human rights message with stakeholders including investors, industry peers and government officials.
COLLABORATE Beyond your comfort zone
Engage other CEOs in your industry to build the leverage needed to change incentives in supply chains at scale.
Establish dialogue and partnerships with stakeholders, including government, international non-governmental organizations and civil society.
Incentivize your team to think about root causes and develop unique collaborations with the power to move the needle on these intractable issues.